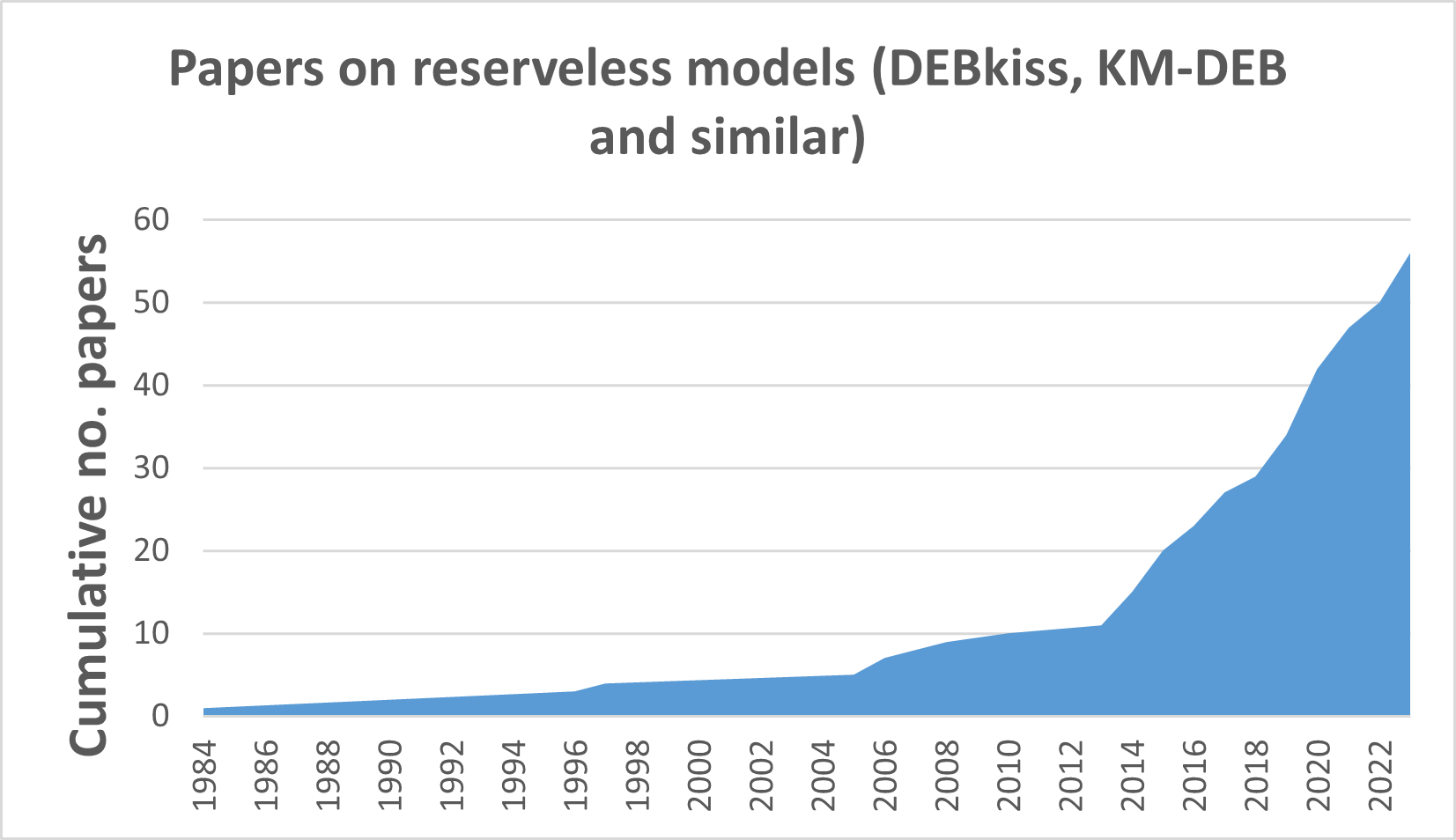
Pre-DEBkiss models; most based on the Kooijman-Metz
formulation.
- Kooijman SALM and Metz JAJ (1984). On the dynamics of
chemically stressed populations: the deduction of
population consequences from effects on individuals.
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 8(3): 254-274. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0147-6513(84)90029-0
- De Roos AM et al. (1992). Studying the dynamics of
structured population models: a versatile technique and
its application to Daphnia. Am Nat 139(1):
123-147. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2462588
- Baveco JM and De Roos AM (1996). Assessing the impact
of pesticides on lumbricid populations: an
individual-based modelling approach. J Appl Ecol 33:
1451-1468. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2404784
- Klok C. and De Roos AM (1996). Population level
consequences of toxicological influences on individual
growth and reproduction in Lumbricus rubellus
(Lumbricidae, Oligochaeta). Ecotox Environ Saf 33:
118-127. http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1996.0015
- Klok C et al. (1997). Assessing the effects of abiotic
environmental stress on population growth in Lumbricus
rubellus (Lubricidae, Oligochaeta). Soil Biol
Biochem 29(3-4): 287-293. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0038-0717(96)00050-8
- Rinke K and Vijverberg J (2005). A model approach to
evaluate the effect of temperature and food
concentration on individual life-history and population
dynamics of Daphnia. Ecol Mod 186(3): 326-344. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2005.01.031
- Klok C et al. (2006). Population growth and
development of the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus
in a polluted field soil: Possible consequences for the
godwit (Limosa limosa). Environ Toxicol Chem
25(1): 213-219. http://dx.doi.org/10.1897/05-286r.1
- Klok C et al. (2006). Does reproductive plasticity in
Lumbricus rubellus improve the recovery of
populations in frequently inundated river floodplains?
Soil Biol Biochem. 38:611-618. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.06.013
- Klok C et al. (2007). Extending a combined dynamic
energy budget matrix population model with a bayesian
approach to assess variation in the intrinsic rate of
population increase. An example in the earthworm Dendrobaena
octaedra. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(11): 2383-2388.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1897/07-223R.1
- Klok C (2008). Gaining insight in the interaction of
zinc and population density with a combined dynamic
energy budget and population model. Environ Sci Technol
42: 8803-8808. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/es8016599
- Jager T and Klok C (2010). Extrapolating toxic effects
on individuals to the population level: the role of
dynamic energy budgets. Phil Trans Royal Soc B 365:
3531-3540. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2010.0137
DEBkiss models (and later models that are closely
related). Full list by year
2013
2014
- Barsi A, Jager T, Collinet M, Lagadic L and Ducrot V
(2014). Considerations for test design to accommodate
energy-budget models in ecotoxicology: a case study for
acetone in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis.
Environ Toxicol Chem 33(7):1466-1475 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/etc.2399
- Hamda NT (2014). Mechanistic models to explore
combined effects of toxic chemicals and natural
stressing factors: case study on springtails. PhD
thesis (Ch. 5 and 6 are DEBkiss
applications).
- Jager T, Barsi A, Hamda NT, Martin BT, Zimmer EI and
Ducrot V. (2014). Dynamic energy budgets in population
ecotoxicology: applications and outlook. Ecol Mod
280:140-147 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.06.024
accepted
version. (Not directly an
application, but reserveless DEB models are mentioned
as a potential building block for population models).
- Jager T, Gudmundsdóttir EM and Cedergreen N (2014).
Dynamic modeling of sub-lethal mixture toxicity in the
nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Sci
Technol 48:7026-7033 http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/es501306t
accepted
version and SI.
2015
- Barsi A (2015). Towards understanding the effects of
putative endocrine disruptors in the great pond snail Lymnaea
stagnalis: experimental and
toxicokinetic-toxicodynamic modelling approaches. PhD
thesis (Ch. 3 and 4 are DEBkiss
applications).
- Fiechter J, Huff DD, Martin BT, Jackson DW, Edwards
CA, Rose KA, Curchitser EN, Hedstrom KS, Lindley ST and
Wells BK (2015). Environmental conditions impacting
juvenile Chinook salmon growth off central California:
an ecosystem model analysis. Geophysical Research
Letters 42(8):2910–2917 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/2015GL063046
- Groeneveld J, Johst K, Kawaguchi S, Meyer B, Teschke M
and Grimm V (2015). How biological clocks and changing
environmental conditions determine local population
growth and species distribution in Antarctic krill (Euphausia
superba): a conceptual model. Ecol Mod 303:78-86.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.02.009
- Jager T and Ravagnan E (2015). Parameterising a
generic model for the dynamic energy budget of Antarctic
krill, Euphausia superba. Mar Ecol Progr Ser
519:115-128 http://dx.doi.org/
10.3354/meps11098. accepted
version and SI.
- Jager T, Salaberria I and Hansen BH (2015). Capturing
the life history of the marine copepod Calanus
sinicus into a generic bioenergetics framework.
Ecol Mod 299:114-120. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.12.011.
accepted
version.
2016
2017
- Desforges JPW, Sonne C and Dietz R (2017). Using
energy budgets to combine ecology and toxicology in a
mammalian sentinel species. Scientific Reports 7:46267.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep46267
(Open Acces, first application for
mammals)
- Jager T, Salaberria I, Altin D, Nordtug T and Hansen
BH (2017). Modelling the dynamics of growth, development
and lipid storage in the marine copepod Calanus
finmarchicus. Marine Biology 164:1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-3030-8
(Open Access)
- Martin BT, Heintz R, Danner EM and Nisbet RM (2017).
Integrating lipid storage into general representations
of fish energetics. J Animal Ecol 86:812-825 http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12667
(closely related, but different from
DEBkiss: removes maturity entirely, and replaces it
with a storage).
- Smallegange IM, Caswell H, Toorians MEM and De Roos AM
(2017). Mechanistic description of population dynamics
using dynamic energy budget theory incorporated into
integral projection models. Methods in Ecology and
Evolution 8(2):146-154. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12675
(more Kooijman-Metz than DEBkiss)
2018
2019
- Boersch-Supan PH and LR Johnson (2019). Two case
studies detailing Bayesian parameter inference for
dynamic energy budget models. Journal of Sea Research
143:57-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2018.07.014
- Hamda NT, B Martin, JB Poletto, DE Cocherell, NA
Fangue, J Van Eenennaam, EA Mora and E Danner (2019).
Applying a simplified energy-budget model to explore the
effects of temperature and food availability on the life
history of green sturgeon (Acipenser medirostris).
Ecological Modelling 395:1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.01.005
- Martin T, H Thompson, P Thorbek and R Ashauer (2019).
Toxicokinetic−toxicodynamic modeling of the effects of
pesticides on growth of Rattus norvegicus. Chem
Res Toxicol 32(11):2281-2294. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.9b00294
(mammal, growth only)
- Martin T, P Thorbek and R Ashauer (2019). Common
ground between growth models of rival theories: a useful
illustration for beginners. Ecological Modelling
407:108712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.05.017
(not really an application, but DEBkiss
is discussed i.r.t. MTE)
- Smallegange IM and MP Berg (2019). A functional trait
approach to identifying life history patterns in
stochastic environments. Ecology and Evolution
9(16):9350-9361. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5485
(Based on Kooijman-Metz)
2020
- Chaparro‐Pedraza, PC and AM de Roos (2020),
Density‐dependent effects of mortality on the optimal
body size to shift habitat: why smaller is better
despite increased mortality risk. Evolution 74: 831-841.
https://doi-org.vu-nl.idm.oclc.org/10.1111/evo.13957
- De Roos, AM (2020). A general approach for analysis of
physiologically structured population models: the R
package 'PSPManalysis'. bioRxiv 2020.06.27.174722. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.27.174722
- Goussen B, C Rendal, D Sheffield, E Butler, OR Price
and R Ashauer (2020). Bioenergetics modelling to analyse
and predict the joint effects of multiple stressors:
meta-analysis and model corroboration. Sci Total Environ
749:141509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141509
(Open Access)
- Jager T (2020). Revisiting simplified DEBtox models
for analysing ecotoxicity data. Ecol Modell 416:108904.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.108904.
accepted
version and SI.
- Pfab F, GV DiRenzo, A Gershman, CJ Briggs and RM
Nisbet (2020). Energy budgets for tadpoles approaching
metamorphosis. Ecol Modell 436:109261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109261
(compares DEBkiss to standard DEB)
- Sherborne N and N Galic (2020). Modelling sublethal
effects of chemicals: application of a simplified
dynamic energy budget model to standard ecotoxicity
data. Environ Sci Technol. 54(12):7420-7429. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00140
- Sherborne N, N Galic and R Ashauer (2020). Sublethal
effect modelling for environmental risk assessment of
chemicals: problem definition, model variants,
application and challenges. Sci Total Environ
745:141027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141027
- Smallegange IM, M Flotats Avilés, K Eustache (2020).
Unusually paced life history strategies of marine
megafauna drive atypical sensitivities to environmental
variability. Frontiers in Marine Science 7:1065. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.597492
(based on Kooijman-Metz)
2021
- Bahlburg D, B Meyer and U Berger (2021). The impact of
seasonal regulation of metabolism on the life history of
Antarctic krill. Ecol Modell 442:109427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2021.109427.
- Chaparro‐Pedraza PC and AM de Roos (2021). Individual
energy dynamics reveal nonlinear interaction of
stressors threatening migratory fish populations. Funct
Ecol 35:727-738. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13751
(uses the model version of Martin et
al 2017)
- Farkas J, LH. Svendheim, T Jager, T Ciesielski, T
Nordtug, B Kvæstad, BH Hansen, T Kristensen and PA
Olsvik (2021). Exposure to low environmental copper
concentrations does not affect survival and development
in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) early life stages.
Toxicology Reports 8:1909-1916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.11.012
- Jager T, J Heuschele, T Lode and K Borgå (2021).
Analysing individual growth curves for the copepod Tigriopus
brevicornis, while considering changes in shape. J
Sea Res 174:102075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2021.102075
(Open Access) (not really an
application, but preparatory work for DEBkiss
analysis, and links nicely to the previous copepod
work)
- Svendheim LH, PA Olsvik, IB Øverjordet, T Jager, TM
Ciesielski, T Nordtug, T Kristensen, BH Hansen, B
Kvæstad, D Altin and J Farkas (2021). Investigating the
effects of marine tailing exposure on the development,
growth, and lipid accumulation of Calanus
finmarchicus. Chemosphere 282:131051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131051
2022
2023
- Bart S, T Jager, S Short, A Robinson, D Sleep, MG
Pereira, DJ Spurgeon and R Ashauer (2023). Modelling the
impact of the pyrethroid insecticide cypermethrin on the
life cycle of the soil dwelling annelid Enchytraeus
crypticus, an original experimental design to
calibrate a DEB-TKTD model. Ecotox Environ Saf
250:114499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114499
open access.
- Croll JC, T van Kooten and AM de Roos (2023). The
consequences of density-dependent individual growth for
sustainable harvesting and management of fish stocks.
Fish and Fisheries 24(3):427-438. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12736
open access.
- Croll JC, T van Kooten and AM de Roos (2023). An
energetic approach to the evolution of growth curve
plasticity. Theor Ecol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12080-023-00571-3
- Pietzsch BW, A Schmidt, J Gröneveld, D Bahlburg, B
Meyer and U Berger (2023). The impact of salps (Salpa
thompsoni) on the Antarctic krill population (Euphausia
superba): an individual-based modelling study.
Ecological Processes 12:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-023-00462-9
- Stevenson LM, EB Muller, D Nacci, BW Clark, A
Whitehead and RM Nisbet (2023). Connecting suborganismal
data to bioenergetic processes: killifish embryos
exposed to a dioxin-like compound. Environ Toxicol Chem
42(9):2040-2053. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5680.
- ...
2024
- Huang A, PJ van den Brink, NW van den Brink and J Baas
(2024). A dynamic energy budget (DEB) model to assess
the sublethal effects of imidacloprid toward Gammarus
pulex at different temperatures. Chemosphere
361:142511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142511.
- Romoli C, T Jager, M Trijau, B Goussen and A Gergs
(2024). Environmental risk assessment with energy budget
models: a comparison between two models of different
complexity. Environ Toxicol Chem 43(2):440-449. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5795
open access.
- Vasbinder K, J Fiechter, JA Santora, JJ Anderson, N
Mantua, ST Lindley, DD Huff and BK Wells (2024).
Size-selective predation effects on juvenile Chinook
salmon cohort survival off Central California evaluated
with an individual-based model. Fisheries Oceanography
33(1):e12654. https://doi.org/10.1111/fog.12654.
- Viaene KPJ, KAC De Schamphelaere and P Van Sprang
(2024). Extrapolation of metal toxicity data for the
rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus using an
individual-based population model. Environ Toxicol Chem
43(2):324-337. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5779.
- ...
|